- Home
- THE BIG PICTURE OF BIOLOGY
- BIG IDEA 1: EVOLUTION
- 1A: Evolution - Change in Genetic Makeup
- 1B: Evolution by Common Descent
- 1C: Life Continues to Evolve
- 1D: Theories of the History of Life
- BIG IDEA 2: ORGANISMS USE ENERGY AND MOLECULES TO GROW, REPRODUCE, AND MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS
- 2A: PHOTOSYNTHESIS, CELLULAR RESPIRATION, AND ENERGY
- 2B: CELL HOMEOSTASIS - CELL MEMBRANE PROCESSES
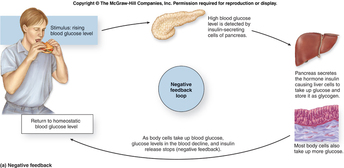
- 2.C: HOMEOSTASIS - POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
- 2.D: Growth and dynamic homeostasis of a biological system are influenced by changes in the system’s environment.
- 2.E: Many biological processes involved in growth, reproduction and dynamic homeostasis include temporal regulation and coordination.
- BIG IDEA 3: LIVING SYSTEMS STORE, RETRIEVE, TRANSMIT, AND RESPOND TO INFORMATION
- 3.A: DNA TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
- 3.B: GENE REGULATION - TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
- 3C: GENETIC MUTATIONS AND VIRUSES
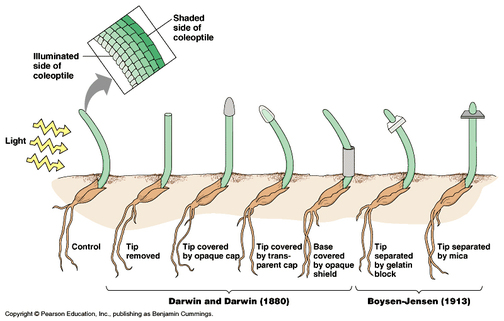
- 3D: CELL COMMUNICATION AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
- 3E: ANIMAL BEHAVIOR AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
- BIG IDEA 4: BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS INTERACT IN COMPLEX WAYS
- 4A: BIOCHEMISTRY AND CELL BIOLOGY
- 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems.
- 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and between components within biological systems affects interactions with the environment.
- RESULTS AND RESOURCES
- AP BIO LABS: BIG IDEA 1 - EVOLUTION
- AP BIO LABS: BIG IDEA 2 -
- AP BIO LABS: BIG IDEA 3
- AP BIO LABS: BIG IDEA 4